
Feeding only breast milk (exclusive breastfeeding) is adequate for baby till 6 months of life. After the age of 6 months, breastfeeding alone is no longer enough for optimal growth and development of the child. Hence, it is necessary to start complementary feeding (CF) along with breast milk. The word “weaning” is now replaced by complementary feeding—the process of introduction of suitable semi-solid food at the right age.
There is a very critical window of opportunity during the first 2 years of life as far as growth and development of child is concerned. The concept of “1000 days” is 9 months of pregnancy plus first 2 years of life during which optimal breastfeeding (for first 6 months of age) and timely and appropriate complementary feeding (at 6 months of age) are extremely important.
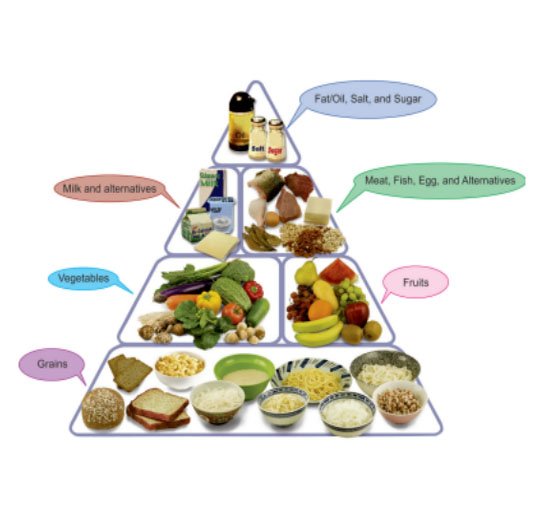
A food containing carbohydrates, proteins, minerals, fats, fibers, vitamins, etc. is “Complete Food” while the food that contains these components in appropriate proportions can be labeled as “Balanced Food”. No food can be labeled as perfectly balanced or complete food. So, in order to make it complete and balanced, there is need to combine various foods in a child’s diet (Fig. 1)


As discussed earlier, after 6 months of life, breastmilk alone is not sufficient to provide adequate nutrition to the child, and one must begin complementary feeding soon after 6 months age completion. Moreover, the jaw biting movement appears app. around 5 months. Swallowing of solid foods occurs around 6–7 months side-to-side movement of tongue develops around 8–12 months. Around 6 months is the ideal time for introduction of complementary feeding or “sensitive period”. If complementary feeding is delayed, then child may enter “critical period” after which infant may always be a poor chewer and may be poor in eating solids later.
The other reasons for complementary feeding starting at 6 months are:
Table 1 Appropriateness of complementary foods for infants.
| Appropriate | Lastname |
|---|---|
| Combination of cereals & pulses (Khichdi, rice,daal etc.), locally available staple foods such as idli, ragi, dosa, dhokla, roti/paratha with oil/ ghee, and some amount of sugar. | *Chocolates, biscuit bread pastry cheese, softy, ice cream, doughnuts, cakes, etc. #Packaged or stored foods,Tinned foods, , artificially cooked foods with preservatives or chemicals |
| Mashed banana, other pulpy fruits (e.g., mango, papaya), sweet potato, and potato | #Fruit juices and fruit drinks |
| Milk-based cereals preparations | *Commercial breakfast cereals |
| Sprouts, pulses, legumes, groundnuts, almonds, cashewnuts, raisins (Note: Any nut should be well grinded and mixed with food as solid pieces may cause choking in young children) | #Repeatedly fried foods containing trans-fatty- acids (which predispose to diabetes, atherosclerosis, obesity, cardiac, and neurological problems in future) |
*These foods must not become the main bulk of complementary foods and may be offered occasionally only.
#These foods should be avoided in children below 2 years of age.
(a) What are the important characteristic of foods for complementary feeding?

(b) What are staple foods?
(c) What precautions are needed while preparing food for complementary feeding?
(d) How to keep food hygienic and safe for feeding?